Data from: A Climatic Sand Management Model for Cardiff State Beach, CA
About this collection
- Extent
-
1 digital object.
- Cite This Work
-
Gopal, Sreeja; O'Reilly, W., C.; Young, Adam; Flick, Reinhard; Merrifield, Mark; Matsumoto, Hironori; Guza, R. T. (2023). Data from: A Climatic Sand Management Model for Cardiff State Beach, CA. UC San Diego Library Digital Collections. https://doi.org/10.6075/J0QF8T29
- Description
-
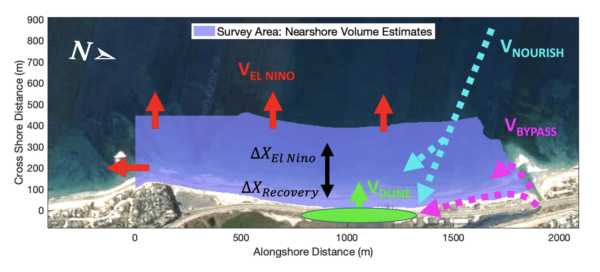
The beach topography and nearshore bathymetry data contained in this object where used to create a sediment budget model and produce the data figures in the paper titled “A Climatic Sand Management Model for Cardiff State Beach, CA” by Gopal et al., 2023.
The data set includes annual mean beach width and nearshore mobile sediment volume estimates between 2000-2019 at South Torrey Pines State Beach and Cardiff State Beach, CA. MATLAB program code to read the data files, model the sediment budget equation in Gopal et al, and recreate the data figures in the paper is also included.
Abstract: An empirically based sediment budget model is developed for Cardiff State Beach CA to assess management strategies to maintain beach width subject to mean sea level rise (MSLR) and potentially more frequent El Niño storms. Two decades (2000-2019) of surveys support the hypothesis that the rocky reefs bounding this beach retain sand added to the nearshore zone, except during strong El Niño years with more severe storm waves. The subaerial beach has widened by ~60 m during the last 20 years owing to nourishment (~17,000 cubic m/yr) of imported sand, and sand bypassed annually by dredging a lagoon inlet at the beach's updrift end. The observed widening yields 1 m/yr of mean beach width increase for each 6 cubic m/m-shoreline of added sand. A strong El Niño year is modeled with a permanent volume loss coupled with a shoreline retreat that recovers partially as the beach profile adjusts between El Niño years. Calibrated with observations from Cardiff and South Torrey Pines (a control beach), the model is used to project beach change through 2050. All modeled scenarios suggest that no bypassing or nourishment (no “management”) will result in tens of meters of beach width loss. However, continued bypassing would partially mitigate MSLR and El Niño beach width losses. An artificially built (living shoreline) dune that backs the beach, if completely undermined during strong El Niño storm waves, stores enough sand to balance one-third of the expected volume loss that year, and may make the beach more resilient and speed subsequent recovery. - Date Collected
- 2000 to 2021
- Date Issued
- 2023
- Authors
- Advisor
- Funding
-
U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (W912HZ1920020) and California Department of Parks and Recreation, Division of Natural Resources Oceanography Program (C19E0026).
- Geographic
- Topics
Format
View formats within this collection
- Language
- English
- Identifier
-
Identifier: Adam Young: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7985-9528
Identifier: Hironori Matsumoto: http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4637-7781
Identifier: Mark A. Merrifield: https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5026-8393
Identifier: R. T. Guza: http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8834-5465
Identifier: Reinhard Flick: https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2830-3527
Identifier: Sreeja Gopal: https://orcid.org/0009-0009-6192-5174
Identifier: W.C. O'Reilly: http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8398-4425
- Related Resources
- Gopal, Sreeja, O’Reilly, W. C., Young, Adam P., Flick, Reinhard E., Merrifield, Mark A., Matsumoto, Hironori, Guza, R. T. (2023). A Climatic Sand Management Model for Cardiff State Beach, CA. Earth’s Future (in review).
- Ludka, B.C., Guza, R.T., O’Reilly, W.C. et al. Sixteen years of bathymetry and waves at San Diego beaches. Sci Data 6, 161 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-019-0167-6
Primary associated publication
Source data
 Library Digital Collections
Library Digital Collections